Quality Management:
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB™)
6 months e-learning + web-based exam
€450 + VAT
“Out of clutter, find simplicity.
From discord, find harmony.
In the middle of difficulty lies opportunity.”
– Albert Einstein
Quality Management:
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB™)
E-learning + Web-based examination
This course is highly recommended for employees and organizations requiring a standardized approach to problem solving for the purpose of continuous improvement in Quality Management.
Key information about this course:
Price: 450€ + VAT ( 6 month E-learning + exam voucher)
- Instructor led video presentations
- Online testing
- Case Studies

Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB™) course focuses on providing students with an understanding of the various Six Sigma and Lean tools and techniques useful to improve the production process and minimize defects in the end product with a greater focus on the practical implementation of these tool and techniques in the organization.
Upon passing the exam, you will be accredited as “Lean Six Sigma Green Belt.”
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB™) – E-learning
Six Sigma in 6 minutes
Six Sigma is a data driven, customer focused, and result oriented methodology which uses statistical tools and techniques to systematically eliminate defects and inefficiencies to improve processes. It is a systematic method to measure and analyze business processes to identify critical factors affecting business results, thereby improving processes, and establishing controls around the improved processes.
Six Sigma is a widely accepted quality concept in the corporate world today. Six Sigma started its journey in the 1980s as a data driven method to reduce variation in electronic manufacturing processes in Motorola Inc. in the USA. Six Sigma became famous when Jack Welch made it vital to his successful business strategy at General Electric in 1995. Today it is used as a business performance improvement methodology all over the world in diverse industries such as general manufacturing, construction, banking and finance, healthcare, education, government, KPO/BPO, and IT/Software. At present IT/ ITES sector companies are dynamically implementing Six Sigma and it is no longer just confined to the manufacturing sector.
The term ‘Six Sigma’ comes from statistics and is used in statistical quality control (SQC) which evaluates process capability i.e. the numerical measure of the ability of a process to meet the customer specifications. It originated from terminology associated with manufacturing which refers to the ability of manufacturing process to produce a very high proportion of output within the given specifications. The sigma rating of a process indicates its yield or percentage of defect-free outputs it produces. A Six Sigma process is the one which produces 99.99966% statistically defect-free outputs which is equivalent to 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).
| Six Sigma Score | Defects per million Opportunities (DPMO) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 308,537 | 69.15% |
| 3 | 66,807 | 93.32% |
| 4 | 6,210 | 99.38% |
| 5 | 233 | 99.98% |
| 6 | 3.4 | 99.9997% |
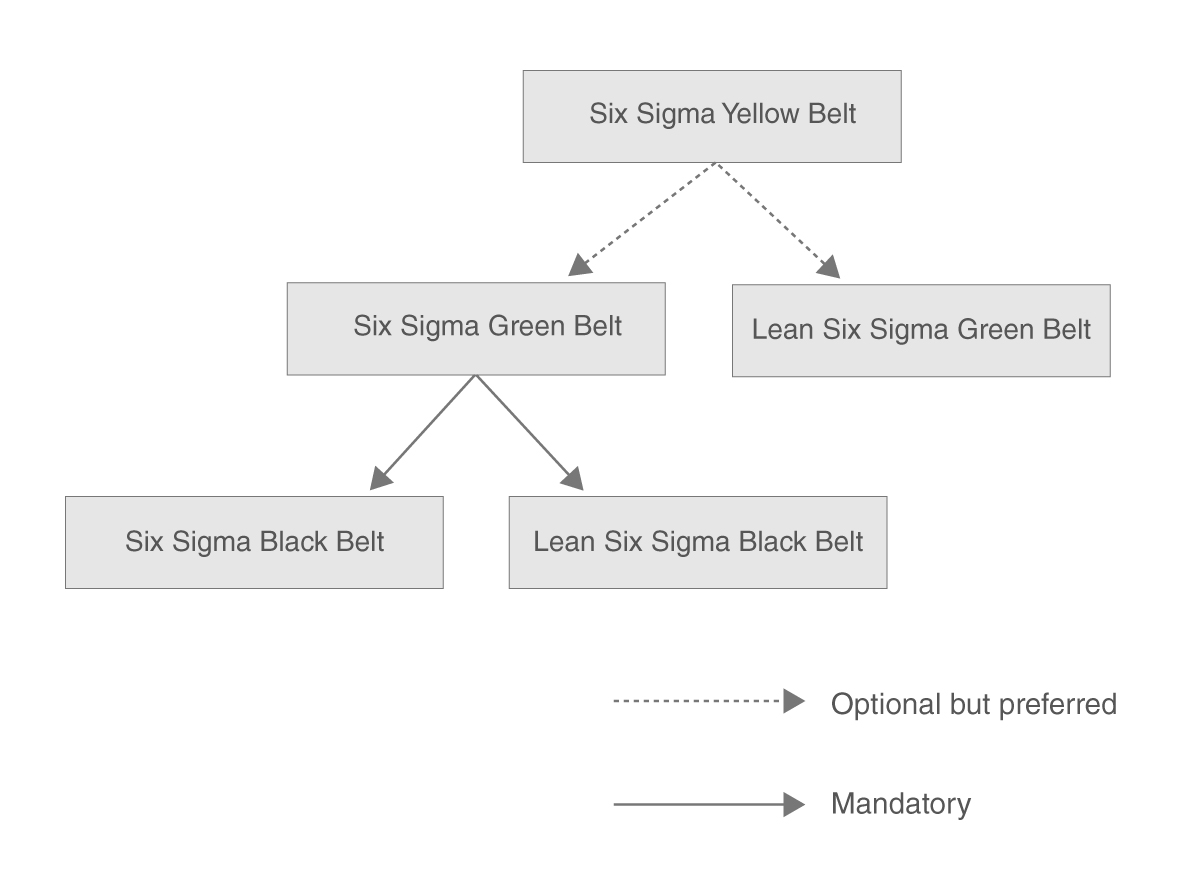
Six Sigma uses a set of quality management and statistical methods and creates a team of experts within the organisation (Executive Leadership, Champions, Black Belt, Green Belt, Yellow Belt etc.) having specific skill sets required to carry out a Six Sigma project. Each Six Sigma project carried out within an organisation follows a defined sequence of phases with quantifiable value targets such as reduction in process cycle time, reduced cost, increase in quality rating / customer satisfaction index, and reduction in defect rate.
Six Sigma Methodologies
There are mainly two methodologies of Six Sigma namely DMAIC and DMADV.
1. DMAIC
DMAIC is a data-driven Six Sigma methodology for improving existing products and processes. The DMAIC process should be used when an existing product or process can be improved to meet or exceed the customer’s requirements. DMAIC methodology consists of five phases: D – Define, M – Measure, A – Analyze, I – Improve, C – Control.
- Define – Define the project targets and customer (internal and external) deliverables.
- Measure – Measure the process to determine the current process performance (baseline).
- Analyze – Find out the root causes of the defects.
- Improve – Improve the process by eliminating defects.
- Control – Control the future performance.
2. DMADV
DMADV is a common DFSS (Design for Six Sigma) methodology used to develop a process or product which does not exist in the company. DFSS is an application of Six Sigma which focuses on the design or redesign of the different processes used in product manufacturing or service delivery by taking into account the customer needs and expectations. DMADV is used when the existing product or process does not meet the level of customer specification or Six Sigma level even after optimization with or without using DMADV. DMADV methodology consists of five phases: D – Define, M – Measure, A – Analyze, D – Design, V – Validate.
- DEFINE the project goals and customer deliverables
- MEASURE the process to determine the current performance level
- ANALYZE and determine the root causes of the defects
- DESIGN the process in detail to meet customer needs
- VALIDATE the design performance and its ability to meet the customer needs