ITIL 4 OVERVIEW & POSTERS
…high-velocity adventures
in Service Management universe!
“If everything seems under control, you’re not going fast enough.” – Mario Andretti
SERVICE MANAGEMENT & ITIL
Services are the main way that organizations create value. Today, most services are IT-enabled and IT service management (ITSM) is considered a key strategic capability!

SERVICE MANAGEMENT
Service Management is a set of specialized organizational capabilities for enabling value for customers in the form of services.

ITIL
ITIL is a collection of best practice recommendations for Service Management and most adopted Service Management framework world wide.

WHY ITIL 4?
Service management is evolving, and so is ITIL.
ITIL 4 (2019) is designed to ensure the system for the effective governance and management of IT-enabled services. It is re-shaping established ITSM practices in the wider context of customer experience, value streams, and digital transformation as well as embracing new ways of working, such as Lean, Agile, and DevOps.
ITIL 4 provides the guidance organizations need to address new service management challenges and utilize the potential of modern technology.

KEY CONCEPTS OF ITIL 4 ARE…
4 DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT
SERVICE VALUE SYSTEM (SVS)

4 DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT
…represent relevant Service Management perspectives that should be considered in everything you do!
4 DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT
ITIL 4 outlines four dimensions in ensuring a holistic approach to service management:
1. Organisations & People
2. Information & Technology
3. Partners & Suppliers
4. Value Streams & Processes
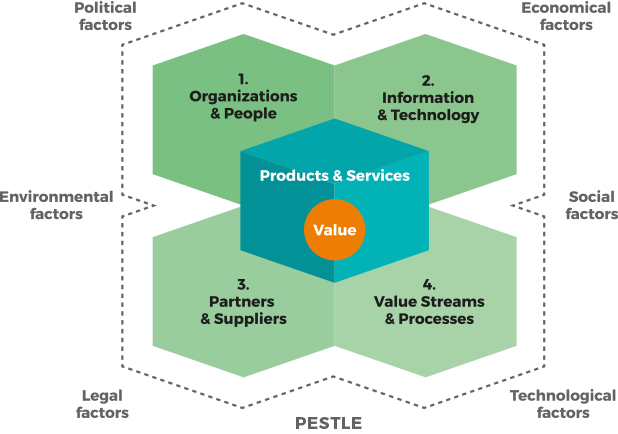
By giving each of the four dimensions an appropriate amount of focus, an organization ensures its Service Value System (SVS) remains balanced and effective.

WHY VALUE STREAMS?
ITIL 2 and ITIL 3 were unintentionally “process siloed”.
ITIL4 introduces Value streams to improve coordination and integration of activities as well as focus on value co-creation. Identifying and understanding the various value streams an organization has is critical to improving its overall performance.

VALUE STREAM
Value stream is a series of steps an organization undertakes to create and deliver products and services to consumers. Value stream is a combination of the organisation’s value chain activities. Value streams define WHAT you do.

PROCESS
Process: A set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs. A process takes one or more defined inputs and turns them into defined outputs. Processes define the sequence of actions and their dependencies. Processes define HOW is it done.
Structuring the organization’s activities in the form of value streams allows it to have a clear picture of what it delivers and how, and to make continual improvements to its services.

SERVICE VALUE SYSTEM (SVS)
… for service management to function properly, it needs to work as a system.
SERVICE VALUE SYSTEM (SVS)
ITIL SVS describes how all the components and activities of the organization work together as a system to enable value creation.
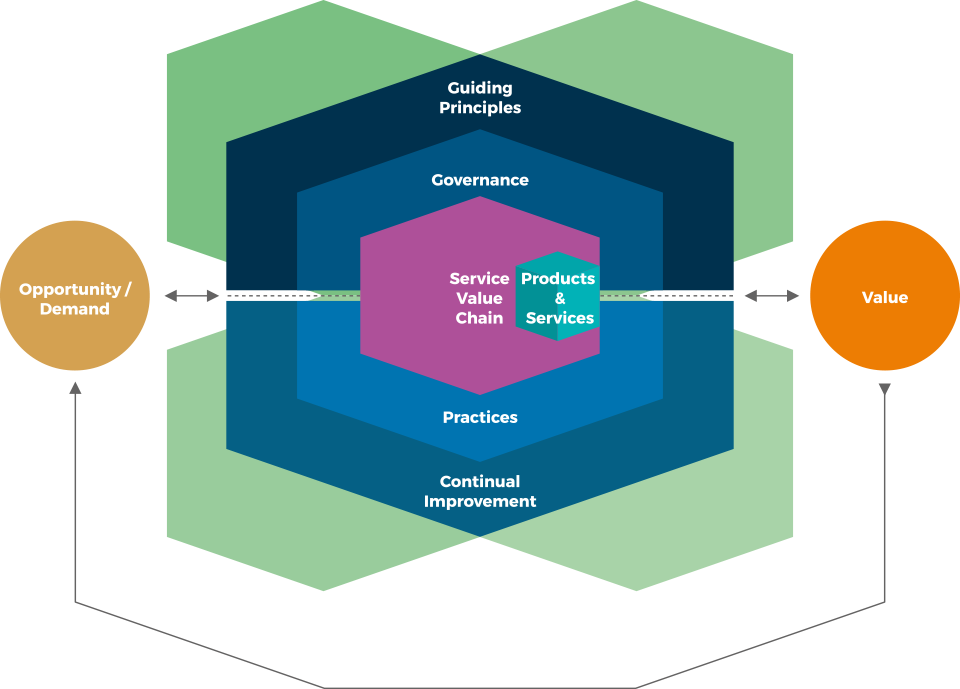

SERVICE VALUE SYSTEM (SVS) – more deatiled
… from OPPORTUNITY/ DEMAND to VALUE …
OPPORTUNITY & DEMAND
PRODUCTS & SERVICES
VALUE
ITIL Service Value System (SVS) enables organizations’ “journey”
from OPPORTUNITY/ DEMAND to achievement of organizational objectives, delivery of SERVICES and finally VALUE co-creation for stakeholders…
… and in order to make this “journey” a successful one, all SVS COMPONENTS must work as a system!…
SVS COMPONENTS
GUIDING PRINCIPLES
GOVERNANCE
SERVICE VALUE CHAIN
PRACTICES
CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT

OPPORTUNITY & DEMAND
Opportunity and Demand trigger activities within the ITIL SVS, and these activities lead to the creation of value.
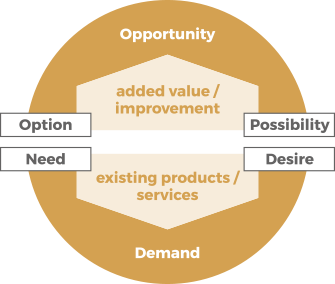

OPPORTUNITY
Opportunities are options or possibilities to add value for stakeholders or otherwise improve the organization.

DEMAND
Demand is a need or desire for products and services among internal and external consumers.

GUIDING PRINCIPLES
Guiding Principles are recommendations that can guide an organization in all circumstances, regardless of changes in its goals, strategies, type of work, or management structure.
ITIL GUIDING PRINCIPLES
…guide organization’s decisions and actions and ensure a shared understanding and common approach to service management across the organization.
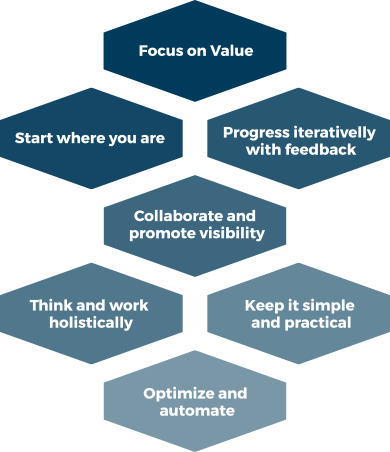

7 GUIDING PRINCIPLES
GUIDING PRINCIPLES…
… guide organizations as they ADOPT a service management approach.
… guide organization as they ADAPT ITIL guidance to their own specific needs and circumstances.
… encourage and support organizations in CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT at all levels.
… allow organizations to effectively INTEGRATE THE USE OF MULTIPLE METHODS into an overall approach to service management.

GOVERNANCE
Organizational governance is a system by which an organization is directed and controlled.
Governance is realized though the activities: Evaluate, Direct, Monitor that enable organizations to continually align their operations with the strategic direction set by the governing body.
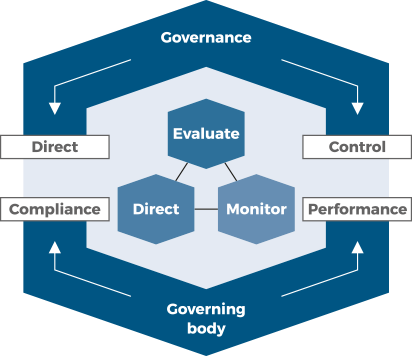

GOVERNING BODY
Governing body is a person or group of people who are accountable at the highest level for the performance and compliance of the organization.

SERVICE VALUE CHAIN
Service value chain is an operating model which outlines the key activities required to respond to demand and facilitate value creation through the creation and management of products and services.
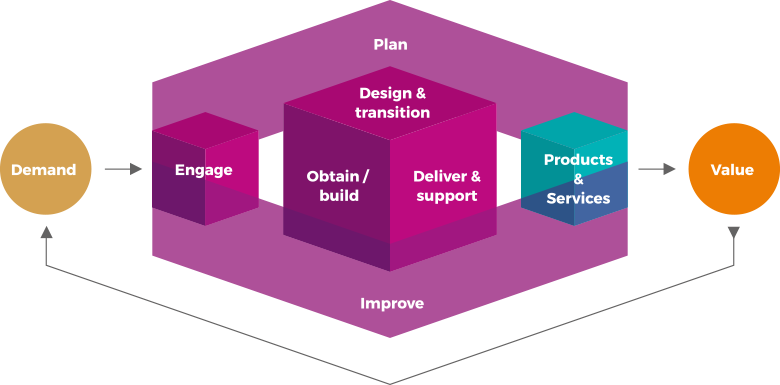
ITIL service value chain includes six value chain activities.

SERVICE VALUE CHAIN ACTIVITIES
PLAN
ensures a shared understanding of the vision, current status and improvement direction for all four dimensions and all products and services across the organization.

IMPROVE
ensures continual improvement of products, services and practices across all value chain activities and the four dimensions of service management.
ENGAGE
provides a good understanding of stakeholder needs, transparency, and continual engagement and good relationships with all stakeholders.

DESIGN & TRANSITION
ensures that products and services continually meet stakeholder expectations for quality, costs and time-to-market.
OBTAIN/BUILD
ensures that service components are available when and where they are needed, and meet agreed specifications.

DELIVER & SUPPORT
ensures that services are delivered and supported according to agreed specifications and stakeholders’ expectations.
Each activity may draw upon internal or third party resources, processes, skills and competencies from one or more practices….

PRACTICES
Sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective. These resources are grouped into the four dimensions of service management.


GENERAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES

SERVICE MANAGEMENT PRACTICES

TECHNICAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES

CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT
Continual improvement is a recurring organizational activity performed at all levels to ensure that an organization’s performance continually meets stakeholders’ expectations.

ITIL CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT MODEL
ITIL continual improvement model provides organizations with a structured approach to implementing improvements.
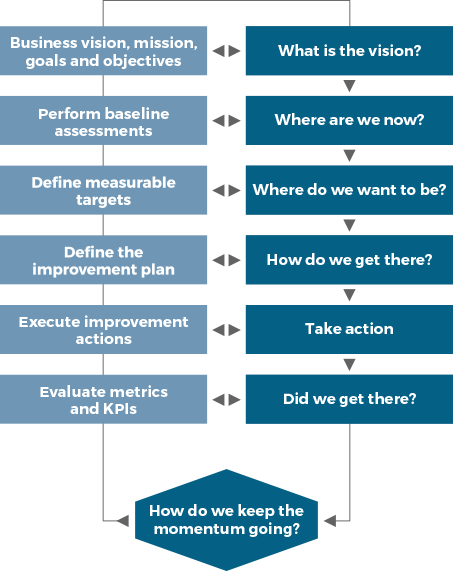
The continual improvement model applies to the SVS in its entirety, as well as to all of the organization’s products, services, service components and relationships.

PRODUCTS & SERVICES

SERVICE
Service is a means of enabling value co-creation by facilitating outcomes that customers want to achieve, without the customer having to manage specific costs and risks.

PRODUCT
A configuration of an organization’s resources designed to offer value for a consumer.
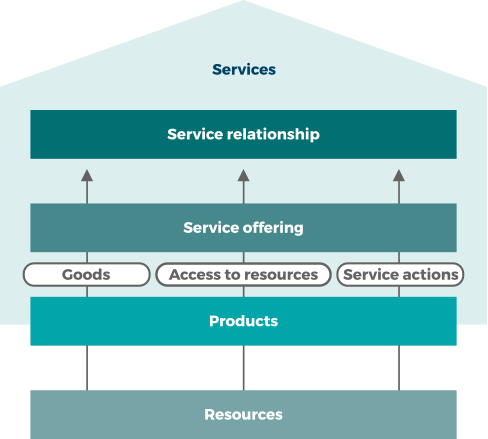

SERVICE OFFERING
A description of one or more services, designed to address the needs of a target consumer group. A service offering may include goods, access to resources, and service actions.

SERVICE RELATIONSHIP
A co-operation between a service provider and service consumer. Service relationships include service provision, service consumption and service relationship management.

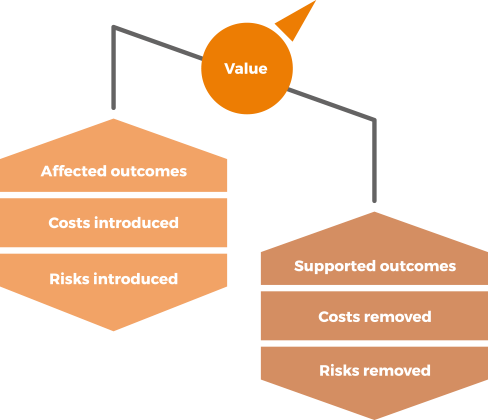
VALUE
Value is the perceived benefits, usefulness and importance of something.
Service relationships are perceived as valuable only when they have more positive effects than negative.

NEGATIVE EFFECTS
Service relationships can introduce new risks and costs, and in some cases, can negatively affect some of the intended outcomes, while supporting others.

POSITIVE EFFECTS
Service providers help their consumers to achieve outcomes, and in doing so, take on some of the associated risks and costs.
OUTCOME, COST & RISK

OUTCOME
Outcome is a result for a stakeholder enabled by one or more outputs.

COST
Cost is the amount of money spent on a specific activity or resource.

RISK
A possible event that could cause harm or loss, or make it more difficult to achieve objectives.
… or uncertainty of outcome.

UTILITY & WARRANTY
From the customer’s perspective, value consists of two primary elements: utility (fitness for purpose) and warranty (fitness for use).

UTILITY
‘what the service does’
The functionality offered by a product or service to meet a particular need. Utility can be summarized as ‘what the service does’ and can be used to determine whether a service is ‘fit for purpose’. To have utility, a service must either support the performance of the consumer or remove constraints from the consumer. Many services do both.

WARRANTY
‘how the service performs’
Assurance that a product or service will meet agreed requirements. Warranty can be summarized as ‘how the service performs’ and can be used to determine whether a service is ‘fit for use’. Warranty often relates to service levels aligned with the needs of service consumers.



